Mosquitoes transmit West Nile Virus. Mosquitoes need water to breed and mature. Even a small amount of water can provide a breeding place for mosquitoes. Mosquitoes hatch and grow in just a few days. There may be breeding places in your yard and around your farmyard.
Though they grow quickly, there are ways to control the mosquito population in your community. Consider these tips to limit the overall population of mosquitoes in your community and to limit your exposure to disease-carrying mosquitoes.
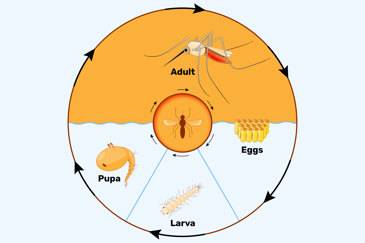
Infographics: WNV: Transmission, Symptoms, & Prevention | Life Cycle of a Mosquito | Prevention in the Yard | Mosquito Repellent Tips
In the Yard
- Keep weeds and tall grass cut short; adult mosquitoes look for these shady places to rest during the hot daylight hours.
- Empty water from buckets, tarps, toys, cemetery urns, water troughs, or other containers.
- Drill holes in the bottom of containers that must be left outdoors, such as garbage cans.
- Fill in tree rot holes and hollow stumps that hold water.
- Wear long sleeves and long pants if you must be in areas with lots of mosquitoes.
- Limit time outdoors from dusk to midnight when Culex mosquitoes are most active.
- Get rid of old tires.
- Get rid of old cans, containers, pots or other water-holding containers on your property.
Chemical Control
- Use mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, oil of lemon eucalyptus, or IR3535 when necessary, following label directions and precautions carefully.
- Some communities use chemicals to kill mosquito larvae and occasionally spray or fog to kill adult mosquito. If you have any questions, call your local mosquito control person.
At the House
- Use a flyswatter or household spray to kill mosquitoes inside buildings.
- Make sure windows and door screens are "bug tight."
- Turn off lights that attract mosquitoes.
- Replace outdoor lights with yellow "bug" lights".
- Check your roof gutters and adjust to eliminate standing water.
Water Sources
- Seal cisterns, septic tanks and fire barrels.
- Fix leaky taps, faucets and sprinklers.
- Change water every other day in birdbaths, fountains, rain barrels, and potted plant trays.
- Aerate ornamental pools or stock them with fish (South Dakota native fathead or killifish minnows).
- Turn over wheelbarrows, or keep them where they will not collect water.
- Treat and clean swimming pools and keep them circulating.
- Drain or fill puddles and low spots with dirt or landscape to reduce standing water.
- Turn over children’s wading pools when not in use.
Pest Resources
- South Dakota Pesticide Program (SD DANR)
- Get certified as a pesticide applicator or find one to do the job for you.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Environmental Protection Agency
- National Pesticide Information Center
- American Mosquito Control Association
- Rutgers University, New Jersey — Center for Vector Biology
- Midwest Center of Excellence for Vector-Borne Disease
