Specimen Source
May be isolated from:
- Blood
All blood cultures should be incubated for a minimum of 21 days. Terminal subcultures should be performed on negative cultures prior to discarding. Subcultures should be incubated for at least 7 days.
- Bone marrow
- Spleen
- Liver
- Abscess material
Brucella is the most commonly reported agent of laboratory-associated infection. It is a virulent, highly infectious organism. Once this organism is suspected on the basis of clinical and/or laboratory information, do not perform additional testing. Send the isolate to the South Dakota State Laboratory for identification.
Gram Stain
Tiny, faintly staining coccobacillus (0.5 to 0.7 by 6.0 to 1.5 microns).
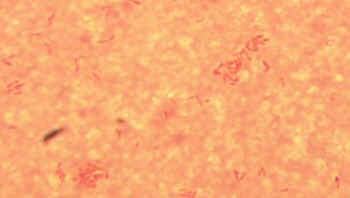
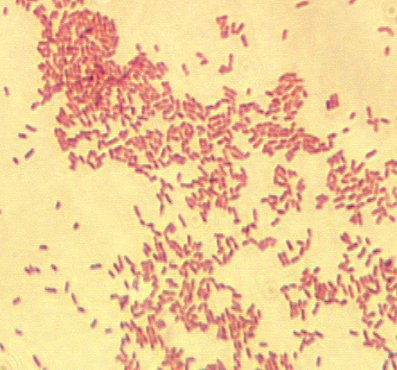
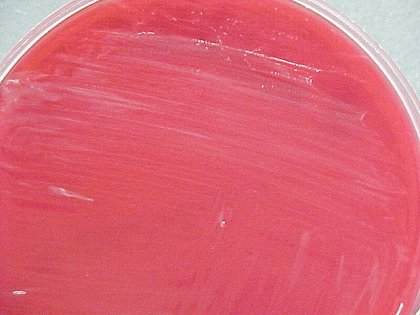
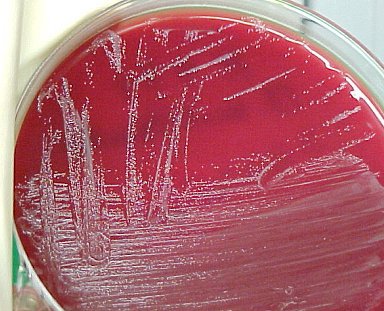
Colony Characteristics
Brucella is the most commonly reported agent of laboratory-associated infection. It is a virulent, highly infectious organism. Once this organism is suspected on the basis of clinical and/or laboratory information, do not perform additional testing. Send the isolate to the South Dakota State Laboratory for identification.
MacConkey – some strains may grow slowly on this media.
Key Characteristics
Brucella is the most commonly reported agent of laboratory-associated infection. It is a virulent, highly infectious organism. Once this organism is suspected on the basis of clinical and/or laboratory information, do not perform additional testing. Send the isolate to the South Dakota State Laboratory for identification.
- Slow growing organisms.
- Faintly staining gram-negative coccobacillus.
- Punctate (minute spots) colonies on sheep blood agar.
- Nonhemolytic.
- Catalase positive.
- Oxidase positive.
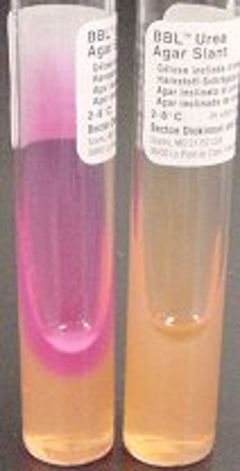
- Urease positive. (May be positive within 1 hour. If not, read at 24 and 48 hours.)
Identification Pitfalls to Avoid
- May be confused with Haemophilus - does not require X/Vfactors.
- Consider the possibility that an organism with characteristics similar to Brucella which is oxidase and urease negative may be Francisella tularensis.
- Brucella isolates may be misidentified by commercially available identification systems, often as Psychrobacter phenylpyruvicus (formerly Moraxella phenylpyruvica).
Look-a-likes (Other OX=/Ur+/GN/Oxidisers)
- Achromobacter
- Acidovorax
- Agrobacterium
- EO-2/EO-3
- Flavobacterium
- Methylobacterium
- Psychrobacter
- Ochrobactrum
- Pseudomonas
- Riemerella
- Roseomonas
- O-2
- II-I
- Oligella
Safety
- Use biosafety level 2 practices for specimen processing.
- Use biosafety level 3 practices for all activities involving the manipulation of cultures.
Brucella is the most commonly reported agent of laboratory-associated infection. It is a virulent, highly infectious organism. Once this organism is suspected on the basis of clinical and/or laboratory information, do not perform additional testing. Send the isolate to the South Dakota State Laboratory for identification.
