Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a rare disease caused by an Orthopoxvirus. Persons with Mpox typically report having close, sustained physical contact with other people who have Mpox. In the recent global outbreak, persons primarily impacted were gay, bisexual, or other men who have sex with men. Anyone who has been in close contact with someone who has Mpox can get the illness. The risk to the general public is low.
Symptoms
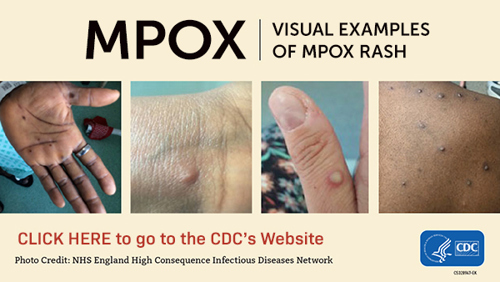
- Rash that looks like pimples or blisters that can occur in the mouth, genital and anal areas, or other parts of the face and body like the hands, feet, and chest.
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle and backaches
- Chills
- Exhaustion
- Swollen Lymph Nodes
Case Counts
CDC Mpox Website: Mpox disease information: symptoms, transmission, and treatment.
Prevention
Take the following steps to prevent Mpox:
- Avoid close skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash that looks like Mpox
- Do not handle or touch materials such as bedding, towels, or clothing of a person with Mpox
- Wash your hands often with soap and water
CDC Resources
Public Health Resources Provider Resources
- Signs and Symptoms: Mpox symptoms usually start within 3 weeks of exposure to the virus. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks. Know the symptoms of Mpox and when to contact a healthcare professional.
- How It Spreads
- Testing
- Prevention
- If You’re a Close Contact
- If You Are Sick
- Vaccines
- What's New & Updated
- Communication Resources